An Italian startup that is supported by a group of scientists develops a V-shaped agrivoltaic system that is said to find an optimal application with bifacial modules and tracking with one axle. It is claimed that the proposed system configuration will reduce land use by 24 % compared to conventional setups.
Italian startup horizonfirm SRL and a group of scientists from the University of Palermo are developing an V-shaped PV array for applications in agrivoltaic projects.
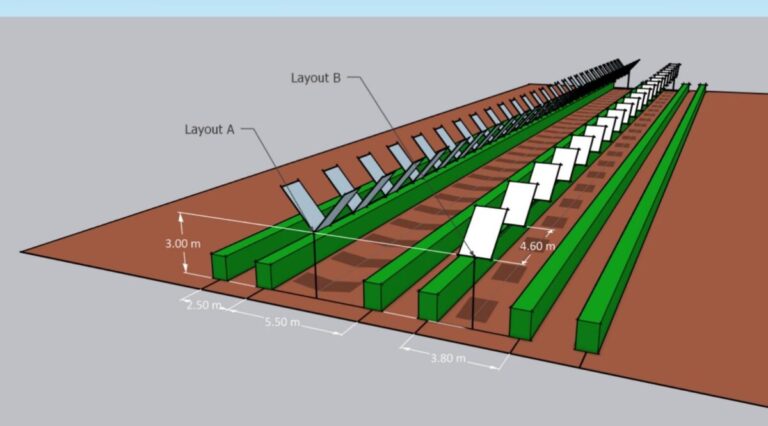
The system has two bifacial modules arranged in a V-configuration with a single axis, which makes the tilt corners dynamically adjusted to optimize the absorption of sunlight and at the same time minimize the shade on crops such as vineyards.
“Although technically feasible with conventional monofacial panels, the V-shaped system is specifically designed to maximize the performance of PV modules with high bifaciality,” said the corresponding author of the research, Valerio Lo Brano, said PV -Magazine. “The unique geometry of the system has been optimized to record both direct and reflected radiation on both sides of the panels, which is impossible with monofacial technology.”
“The use of monofacial panels would significantly endanger the yield of the system, which is fundamental to the value proposition of the V-configuration,” he also explained. “The design will achieve its maximum performance potential when 100% bifaciality modules are available in the market, because this would fully use the system of the system to capture reflected light. The system has been dimensioned for the most common panel size that is currently on the market with a bifaciality factor of at least 80% with which the compations with which the compations the compations with which the compations the compations, with which the compations are the compations the compations, the compations the compations, the compations the compations, the compations with which the compations of the compations the compations, the compations of the compations, the compations of the compations with which the compations of the compations of the compations of the compations of the compations of the compations of the compations of the compations with which the compations of the compations of the compations. Manufacturers are guaranteed. “
In the newspaper “Modeling and analysis of V-shaped bifacial PV systems for agrivoltaic applications: a python-based approach to energy optimization“Published in Applied energyThe researchers said that one of the most important contributions of their work is the establishment via the PVLIB software of a Adapted Python-based algorithm specifically tailored to the proposed V-shaped configuration. This tool can model the system performance of the system, good for mutual shadow, multiple reflections and ground alge.
“It’s the First-in-in-sort Python algorithm, “Lo Brano emphasized.” It also simulates several reflections and dynamic tilt adjustments, two functions that are absent in commercial tools. “
In the proposed system configuration, PV panel slopes can have a tilt angle of 50 ° and 90 °, whereby the top line of the V-shaped cone is placed 3 m above the ground. The Azimutoek of the modules must be correctly determined by the project developer, because the system cannot be used with Azimuthal trackers.
Image: Horizonfirm SRL, Applied Energy, CC by 4.0
Simulations in Palermo, Italy, showed that the system generates 2089.3 kWh/year per panel pair, which is 5.2% less than conventional setups but with 24% land savings. The scientists also discovered that the system drastically reduces land occupation by 24%.
“When it was scaled to a vineyard with one hectare, the system achieved an annual energy production of 551.6 MWH, almost double the 286.5 MWh generated by a configuration with a row of rows,” she added and noticed that they noticed that that The system can be adapted to various Agrivoltaic scenarios and crops such as grapes, olives or leafy vegetables that thrive under partial shade, whereby the adjustable tilt of the system the shadow minimizes during critical growth diodes.
The University of Palermo and Horizonfirm are currently implementing a pilot project of 949 KW with the proposed system configuration.
‘The project is planned for the end of the year and is being developed in collaboration with Trina Solar for module offer and Huawei Technologies for Smart Inverters, ”said HorizonFirm partner and director, Christian Chiaruzzi, PV -Magazine. “The Huawei systems will manage the tracking -algorithm via an independent PLC controller. Moreover, we currently have three projects in progress that use fixed subvertical slope structures. “
Horizonfirm recently patented the PV system design. ‘The patent idee stems from the growing acceptance of bifacial photovoltaic modules, “Chiaruzzi explained.” It is important to note that bifacial modules currently do not have higher costs per kW compared to monofacial alternatives. That is why the increased initial investment would only be related to the structural components of the V-system, including the tracking mechanism. “
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to work with us and reuse part of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content