In a new weekly update for pv magazineSolcast, a DNV company, reports that August was an exceptional month for solar production in the southeastern states, while regions such as the Midwest and Northeast experienced cloudier conditions and lower irradiance.
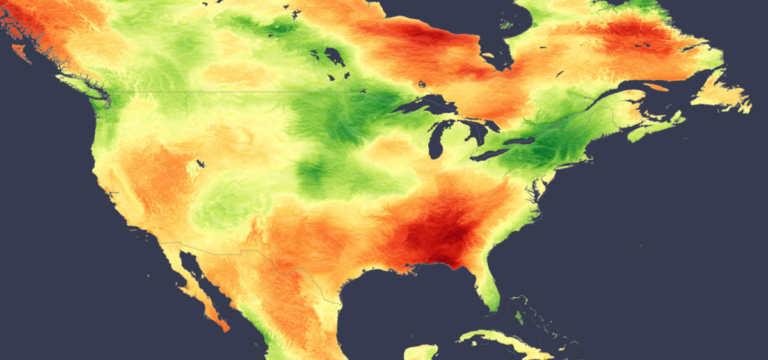
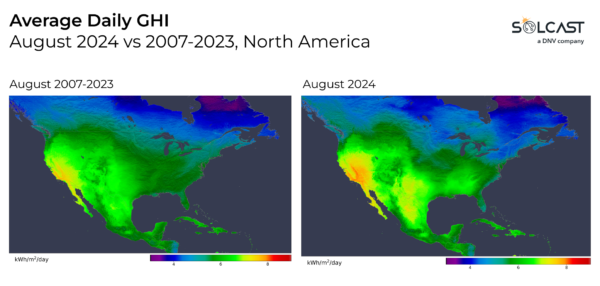
August 2024 was an extraordinary month for solar energy production in the southeastern states. A dominant high-pressure ridge over most of the US, especially over the Southern Plains and southern states, resulted in record-breaking heat and radiation levels, according to analysis using the Solcast API. Meanwhile, regions such as the Midwest and Northeast experienced cloudier conditions and lower insolation due to the interaction between the jet stream and the high-pressure system.
A ridge of high pressure persisted across the continent throughout August, bringing clear skies and above-average insolation to the southern US. States including Tennessee, Mississippi, Georgia and Alabama saw irradiation levels up to 130% of their climatological average, with Atlanta recording the highest average daily irradiation in August since 2007.
These clear-sky conditions followed a pattern of record temperatures and drought, as many southern states experienced exceptionally warm and dry conditions that lasted throughout the month.
In contrast, the situation was very different in the Midwest, Northeast and parts of lower Quebec, where conditions were cloudier. The high-pressure ridge directed the jet stream further north, allowing low-pressure systems and cold fronts in the Pacific Ocean to converge over these areas, with the warm air resulting in cloud cover, heavy rain and insolation 20% below average. Particularly in the northeastern US, there were frequent showers that significantly reduced the potential for solar energy generation.
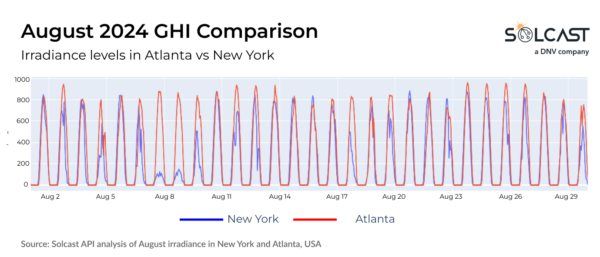
The above graph shows the large difference in radiation intensity between Atlanta and New York. Atlanta, which benefited from a nearly month-long streak of clear skies, consistently recorded higher and more stable irradiance in August. In contrast, New York’s radiation level shows significant daily fluctuations, with many days of low radiation due to cloud cover. Including August’s catastrophic slow-moving system that caused flooding in the Northeast.
Solcast produces these figures by tracking clouds and aerosols worldwide at a resolution of 1-2 km, using proprietary satellite data AI/ML algorithms. This data is used to drive irradiance models, allowing Solcast to calculate high-resolution irradiance, with a typical deviation of less than 2%, as well as cloud tracking predictions. This data is used by more than 300 companies that manage more than 150 GW of solar energy worldwide.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of the author pv magazine.
This content is copyrighted and may not be reused. If you would like to collaborate with us and reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content