De Zoantellel was developed by an international team, including the Kaust of Saudi Arabia and the Chinese Academy of Science.
An international research team led by the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) in Saudi Arabia has developed a 3D/2D perovskite solar cell based on a meta-amidinopyridine (MAP) Ligand that allegedly the Ferroelectric properties and passivation effects Can improve at the Cell’s 3D/2D interface without deteriorating loading transport.
Perovskiet cells built with 2D hybrid materials are known for their stability and show large exciton -binding energy compared to conventional 3D devices. Various organic ammonium salts have been tested to develop 3D/2D sun cells, with Halogenated Analogues of Fenethylammonium Jodide (Pei) salts that are the preferred choice because of their potential to improve gatextraction.
The researchers explained that 3D/2D Perovskiet heterostructures are currently being formed by resolving suitable ligands in polar solvents, which influence cargo transport and cell stability. To tackle this problem, they used maps and the post-dropping of the solvent, which resulted in a “highly ordered” 2D perovskiet phase on the surface of a 3D-Persovskiet film, without the quality of the entire 3D/2D folder- to endanger the film considerably.
“2D folder without treatment with post-dipps shows an unordered orientation of the 2D phase on top of the 3D-Perovskiet,” they explained further. “On the other hand, after dripping solvents, the 2D folder monster shows a more ordered 2D phase parallel to the 3D perovskiet layer with a more infiltrated structure.”
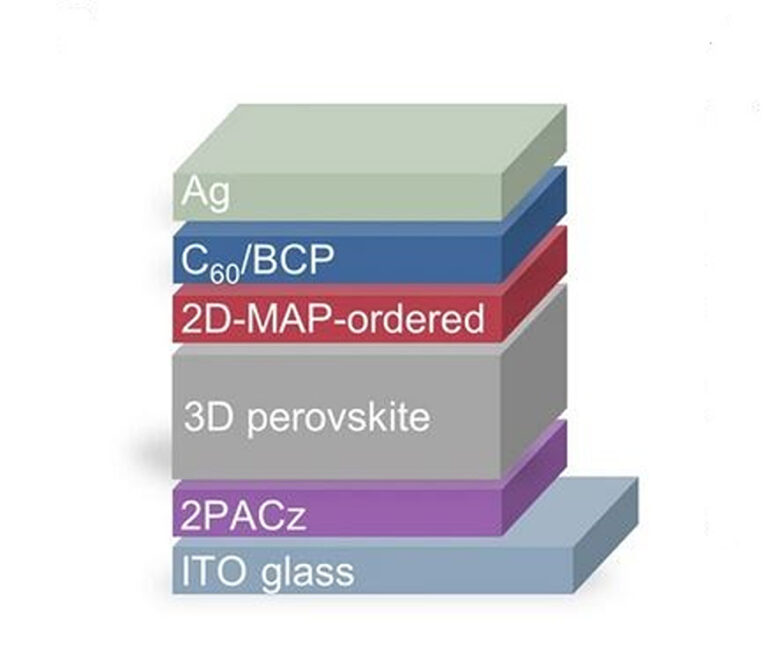
The research team built the solar cell with a substrate made of glass and indium tinoxide (ITO), a hole transport layer (HTL) on the basis of 2Pacz, a 3D perovskietabsorber, a 2D perovskiet layer, an electrontransport layer (ETL) based on Buckminsterfullerene (C60), a buffer layer of BathocuProine (BCP) and a silver (AG) metal contact.
“The ordered 3D/2D-map-based devices show the largest potential drops and electric field improvement in the perovskiet/C60 Contact, benefit from the improved Ferro electricity of the ordered 2D-map layer, “the scientists emphasized. “Moreover, the electric field ratio between the perovskiet/C is60 And ITO/SAMS/PEROVSKIET interfaces increased. “
Tested under standard lighting conditions, the solar cell reached a maximum power conversion -efficiency of 26.05%, a certified efficiency of 25.44%and a filling factor of 85.5%. For comparison, a benchmark solar cell without the 2D folder achieved efficiency of 23.5 and a filling factor of 81.45%.
“Under humid heat and outside tests, the encapsulated perovskiet keep solar cells 82% and 75% of their initial efficiency after 1,000 hours and 840 hours respectively, which demonstrates improved practical sustainability,” the researchers said. “These results confirm the compatibility of our method with scalable deposition processes.”
The design of the solar cell was presented in the study “Modulated 3D/2D heterosexual structures of drip-drug drip for powerful perovskite solar cells“Published in Nature communication. The research group included academics from the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shanxi Normal University, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Korea University and the National Technical University of Athens in Greece.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to work with us and reuse part of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.