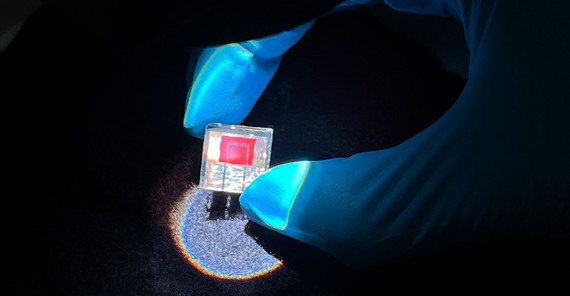
The tandem cell was devised by a research team from Germany’s University of Potsdam and the Chinese Academy of Sciences and is based on a perovskite bottom cell with a wide band gap and an organic top device with a narrow band gap. The researchers used a compound known as cyclohexane 1,4-diammonium diiodide for surface passivation.
Researchers from the University of Potsdam in Germany and the Chinese Academy of Sciences claim to have achieved a record-breaking energy conversion efficiency of 25.7% for a tandem solar cell based on a wide bandgap perovskite bottom cell and a narrow bandgap organic top device.
The scientists highlighted that using an organic cell as a soil device offers the advantage in terms of a low ecological footprint compared to cell technologies based on crystalline silicon or thin films of copper, indium, gallium and selenium (CIGS), which require high processing temperatures are.
“Perovskite and organic solar cells are both processed at low temperatures,” the group said.
It synthesized a new red/infrared-absorbing organic solar cell that reportedly extends its absorption even further into the infrared. “Yet, tandem solar cells were limited by the perovskite layer, which exhibits strong efficiency losses when adjusted to absorb only blue/green parts of the solar spectrum,” the academics explained. “To address this, we used a new passivation layer applied to the perovskite that reduces material defects and improves the performance of the entire cell.”
Image: University of Potsdam
The scientists built the tandem cell with a glass substrate, a recombination layer of transparent conducting oxide (TCO) that integrates a self-assembled monolayer, a perovskite absorber with an energy band gap of 1.88 eV, the new passivation layer, a junction layer (ICL), an organic absorber with an energy band gap of 1.27 eV, a PDINN, a cathode interlayer intended to form the interface between the active layer and the upper electrode, and a silver (Ag) electrode.
They also used cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium diiodide (CyDAI2) as a surface passivator. This compound naturally contains two isomeric structures with ammonium groups on the same or opposite sides of the hexane ring and the two isomers exhibit completely different surface interaction behavior,” they explained, noting that this helps to reduce the quasi-Fermi level splitting open circuit voltage reduce. mismatch of the perovskite cell.
Tested under standard lighting conditions, the tandem cell achieved an energy conversion efficiency of 26.4% and a certified efficiency of 25.7%. The result currently represents a world record for this cell technology.
The new cell concept was introduced in the paper “Isomer diammonium passivation for perovskite-organic tandem solar cells”, published in nature.
This content is copyrighted and may not be reused. If you would like to collaborate with us and reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.
Popular content